Use VPC Endpoint to Keep Your Network Traffic in AWS
AWS VPC Endpoints enhance security and performance by keeping network traffic within the AWS cloud.
This article covers what VPC Endpoints are, their types, and how to set them up to improve your AWS infrastructure.
1. Introduction
Recap of AWS VPC Basics
AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) allows you to create a logically isolated network within the AWS cloud. You can control your network’s IP address range, subnets, route tables, and network gateways.
This isolation helps secure your AWS resources and manage network traffic effectively.
Importance of VPC Endpoints
VPC Endpoints are crucial for maintaining secure, private connectivity between your VPC and AWS services.
They prevent your data from traversing the public internet, thus enhancing security and often improving performance.
2. In-Depth Look at VPC Endpoints
Detailed Definition
VPC Endpoints are virtual devices that enable you to connect to AWS services directly from your VPC without using public IP addresses. This connection is made through a private link within the AWS network, enhancing security and performance.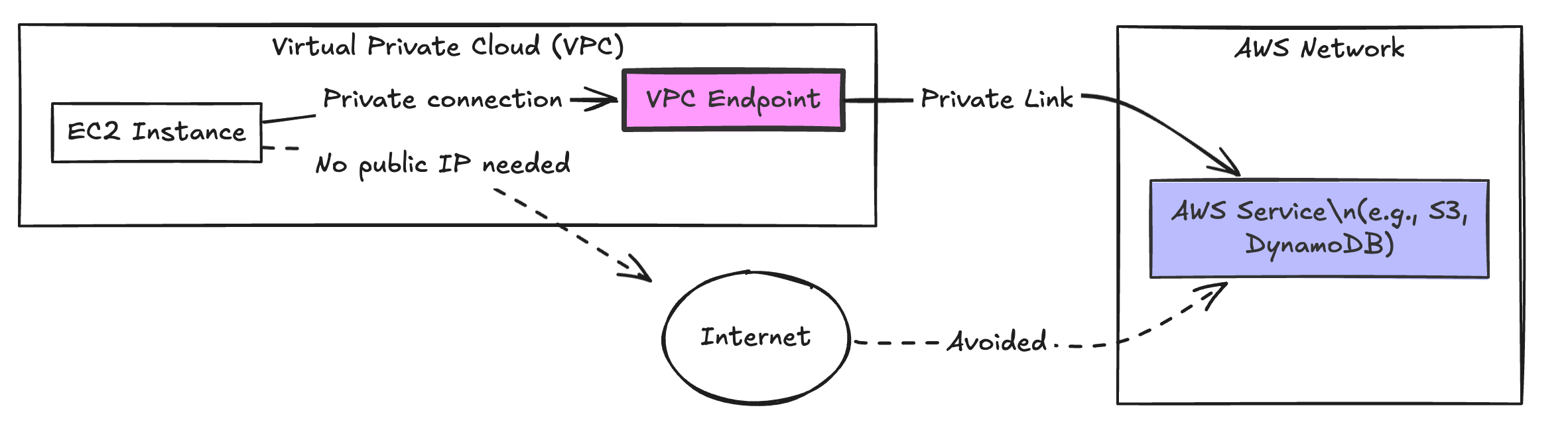
Types of VPC Endpoints
- Interface Endpoints (AWS PrivateLink)
- Architecture and Use Cases: Interface Endpoints use elastic network interfaces (ENIs) with private IP addresses to connect to AWS services or other VPC endpoints. They are ideal for accessing AWS services like API Gateway or third-party services hosted on AWS, keeping traffic within the AWS network.
- How They Work: An ENI is created in your subnet, which you use to access the service. The traffic to the service is routed over a private link, providing secure and low-latency access.
- Gateway Endpoints
- Architecture and Use Cases: Gateway Endpoints provide a gateway for traffic destined for S3 and DynamoDB. They integrate with your route tables, allowing traffic to these services to stay within the AWS network.
- How They Work: When you configure a Gateway Endpoint, you add a route to your route table that directs traffic for S3 or DynamoDB to the endpoint. This configuration avoids the public internet and reduces exposure to potential threats.
3. Use cases
Scenario 1: Access a custom service in another VPC
If you have two VPCs (VPC A & VPC B), and you want EKS in VPC A to access a custom service running in VPC B, you have multiple options depending on your security and networking requirements. Here’s how you can use VPC Endpoints to achieve this securely.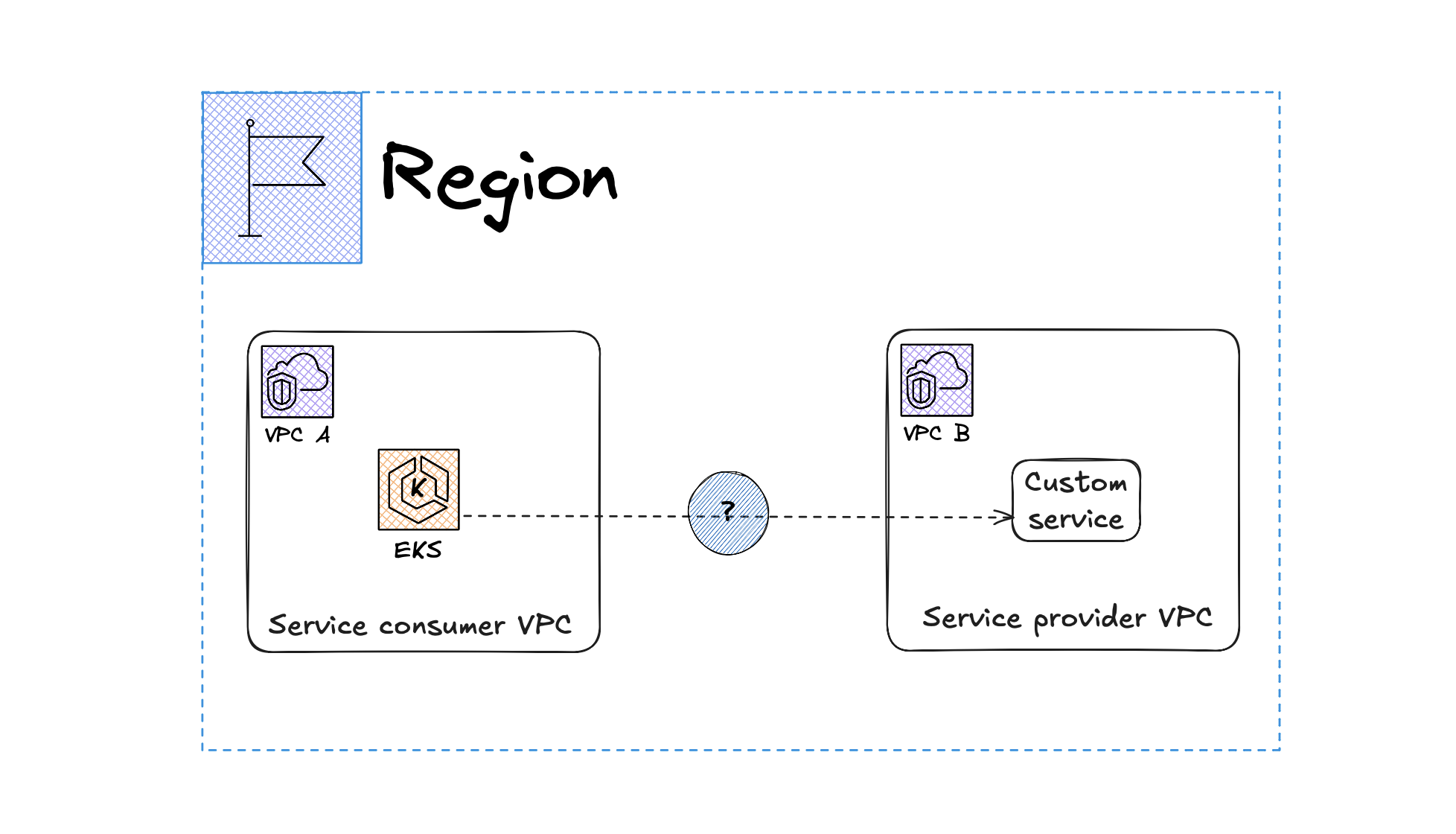
🔍 AWS PrivateLink Architecture
1️⃣ In VPC B (Service Provider)
- Deploy the custom service behind an NLB.
- Expose it via a VPC Endpoint Service.
2️⃣ In VPC A (Client)
- Create an Interface VPC Endpoint in VPC A.
- AWS automatically provisions an ENI inside VPC A.
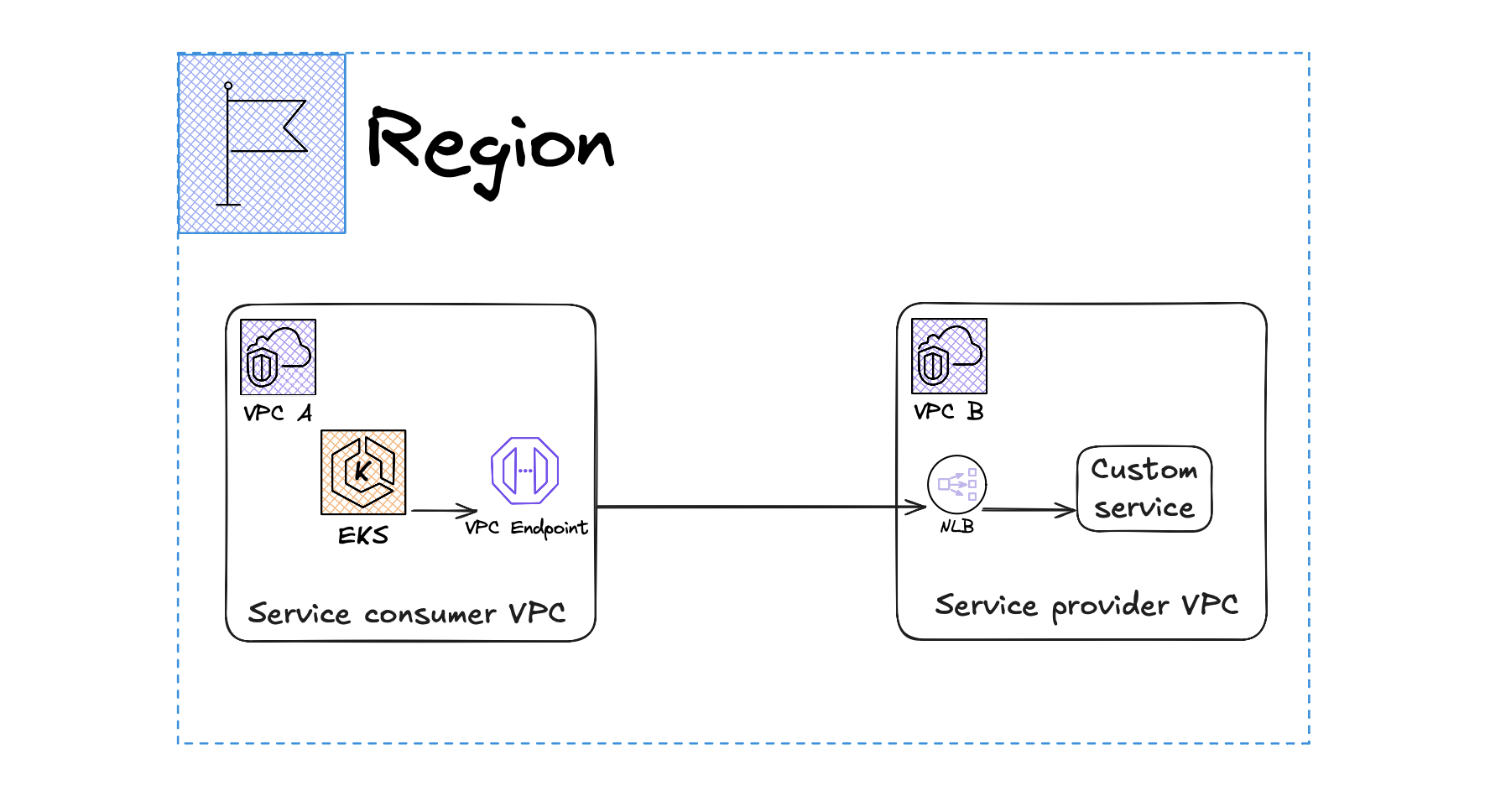
3️⃣ How Traffic Flows
- EKS pods in VPC A send traffic to the ENI (Interface Endpoint) inside VPC A.
- The ENI forwards the request securely to the NLB in VPC B.
- The NLB routes the request to the backend custom service in VPC B.
4. Conclusion
Summary of Benefits
- Enhanced Security: VPC Endpoints keep your network traffic within the AWS cloud, reducing exposure to potential threats.
- Improved Performance: By avoiding the public internet, you can achieve lower latency and higher throughput.
- Simplified Networking: VPC Endpoints provide a straightforward way to connect to AWS services securely.
- Cost-Effective: Using VPC Endpoints can help you save on data transfer costs and reduce the need for NAT gateways.